User Guide
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Using the user guide
- 3 Quick start
-
4 Features
- 4.1 Contact Management
-
4.2 Meeting Management
- 4.2.1 Adding a meeting:
addmeeting - 4.2.2 Adding a participant into a meeting:
addpart - 4.2.3 Delete a participant into a meeting:
deletepart - 4.2.4 Listing all meetings:
listmeeting - 4.2.5 Editing a meeting:
editmeeting - 4.2.6 Finding meetings:
findmeeting - 4.2.7 Deleting a meeting:
deletemeeting - 4.2.8 Clearing all meetings :
clearmeeting - 4.2.9 Remind meetings:
remindmeeting - 4.2.10 Exporting meetings in .ics format :
exportmeeting - 4.2.11 Automatic meeting reminder
- 4.2.1 Adding a meeting:
- 5 General
- 6 FAQ
- 7 Command summary
- 8 Prefix summary
- 9 Glossary
1 Introduction
1.1 About Recretary
done by: Tan Xuan Zhi
Hello, fellow secretaries!
Welcome to Recretary, a desktop application to help you manage contacts and meetings so that you can be freed from these tedious tasks.
If you are still keeping track of your contacts and meetings manually and find that tiresome, then Recretary is the solution for you! Recretary is specially customised for secretaries to make the contact and meeting management process as easy and as error-free as possible. What’s more, Recretary is primarily optimized for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI), which means that you can use most features with just a single line of command. If you can type fast, will be able to manage your contacts and meetings much more efficiently on our sleek Graphical User Interface (GUI).
If you are new to CLI or Recretary, fret not! Explore our User Guide now to find out more on our amazing features and how they work!
1.2 Overview of the User Interface
done by: Adithya Narayan Rangarajan Sreenivasan
As you can see in in the figure below (Fig 1.1a), the user interface of the app is sleek and beautiful, but still gives you all the information that is required. The contacts are arranged in the left and the meetings are arranged in the right. All the meetings are always sorted according to time (earliest first). The meeting timeline draws your attention into the current time and the next meeting that is scheduled to take place.
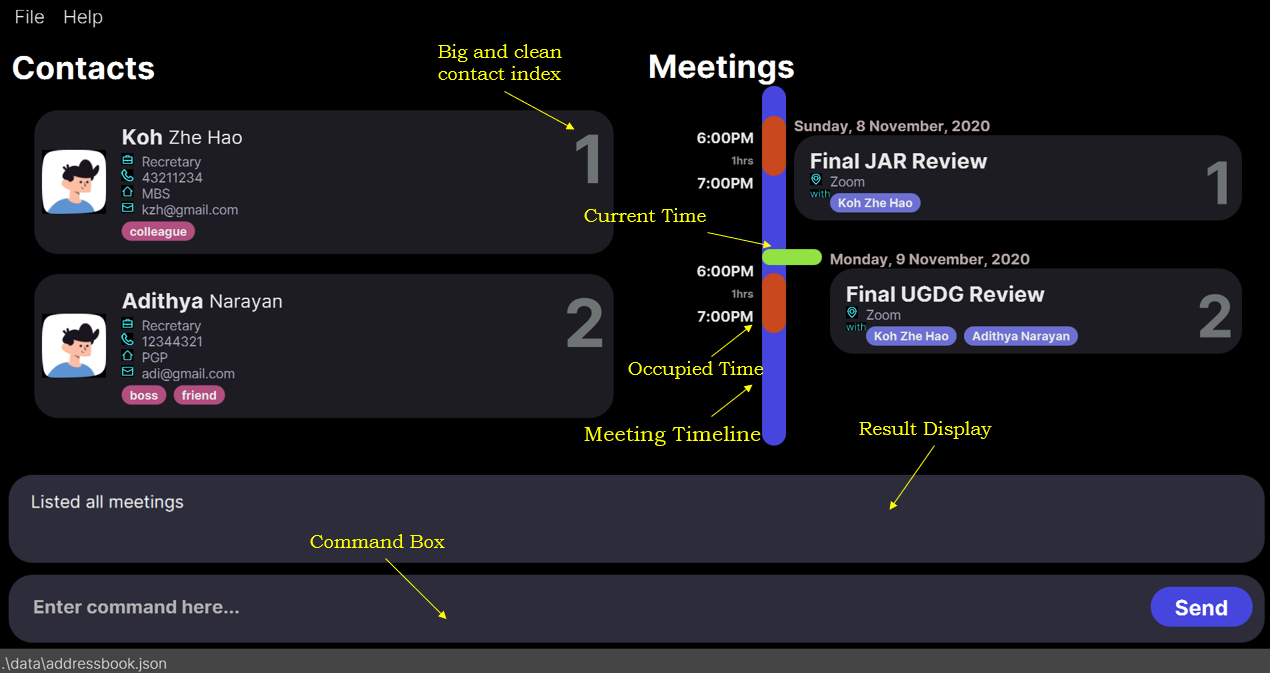
To ensure maximum efficiency, we have made the app default to a full screen. The app has been made keeping full screen usage in mind.
2 Using the user guide
done by: Adithya Narayan Rangarajan Sreenivasan
This section will give you, the user, all the details required to interpret and understand the user guide and use it to your advantage. This guide encompasses all the features that the app provides with in-depth explanation on how to use them in the app with examples and illustrations.
2.1 Format
done by: Adithya Narayan Rangarajan Sreenivasan
| Symbol/Formatting | Explanation |
|---|---|
Monospaced Codeblocks (eg: example) |
User input, command box output |
| A tip to increase your efficiency | |
| Notes. An important must read before you execute a command | |
| Visual Walkthrough. Images to guide you through an example use of the command step by step |
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inaddcontact n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asaddcontact n/John Doe. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.gn/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times.
e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used as ` ` (i.e. 0 times),t/friend,t/friend t/familyetc. -
Parameters with prefixes can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesINDEX n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,INDEX p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable whereasp/PHONE_NUMBER INDEX n/NAMEis not correct sinceINDEXhas no prefix. -
Although it is not recommended to supply duplicate parameters, they will still be accepted. However, only the last parameter of the same type will be considered.
e.g. if the command entered by user iseditcontact 1 n/John n/Bob, onlyn/Bobwill be considered as only the last of the twon/parameters is considered.
2.2 Navigation
done by: Adithya Narayan Rangarajan Sreenivasan
This user guide was made taking in mind the ease of usability and navigation. You can easily click on the headings and sub-headings in the table of contents (and also other parts where a heading is mentioned) and it will take you right into the required part of the guide.
Here is a quick summary of relevant links you can take a look at if you wish to brush through the user guide.
- Get up and running as soon as possible: Quick Start
- For a summary of the features on this user guide: Command Summary
- For a summary of the prefixes of commands: Prefix Summary
3 Quick start
done by: Liu Chuyue
This section contains a step-by-step guide on how to install Recretary on your computer, as well as some basic commands for you to get familiarised with Recretary.
3.1 Installation
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
recretary.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for Recretary.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data. You can get familiar with our app by following the simple instructions below and observe the changes in your GUI. You can also just type
clearcontactandclearmeetingseparately to clear all data and immediately start using the app.
-
For you to get familiar with the app and to practice, type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window. Some example commands you can try:-
listcontact: Lists all contacts. -
addcontactadd_contact n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 c/ABC Holdings Pte. Ltd: Adds a contact namedJohn Doeto the Contacts List. -
deletemeeting1: Deletes the 1st meeting shown in the current list. -
clearmeeting: Deletes all meetings. -
clearcontact: Deletes all contacts. -
exit: Exits the app.
-
-
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
4 Features
This section contains detailed information of each of Recretary’s commands, with relevant examples and images to guide you.
4.1 Contact Management
done by: Koh Zhe Hao
Storing and using contact entries in Recretary is similar to the way a phonebook stores your contacts’ phone numbers. However, Recretary improves upon traditional phonebooks by taking multiple fields of information such as name, phone number, email, address and company into consideration. There are also optional entries, company roles and tags(usually a short phrase used to describe someone), that may help you organize your contacts better. The commands listed below are various methods you can manage your contacts. You can also find your list of contact information on the left-hand-side of the window as shown in the highlighted section from the picture below.
Note: You can view all contacts by hovering your mouse at the highlighted section, and simply scrolling up or down to view more contacts in the list.
4.1.1 Adding a person: addcontact
done by: Koh Zhe Hao
The most fundamental command for contact management in Recretary. It simply allows you to add a new contact into Recreatary. A contact here represents the collection of all information from a single person.
Note: Do take note of the requirements on the fields listed below as specified by Format and Prefix Summary.
Format: addcontact n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS c/COMPANY [r/COMPANY_ROLE]… [t/TAG]…
Examples:
addcontact n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 c/ABC Holdings Pte. Ltdaddcontact n/Betsy Crowe t/friend e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Mansion p/1234567 r/CEO c/DEF Company
Example Usage
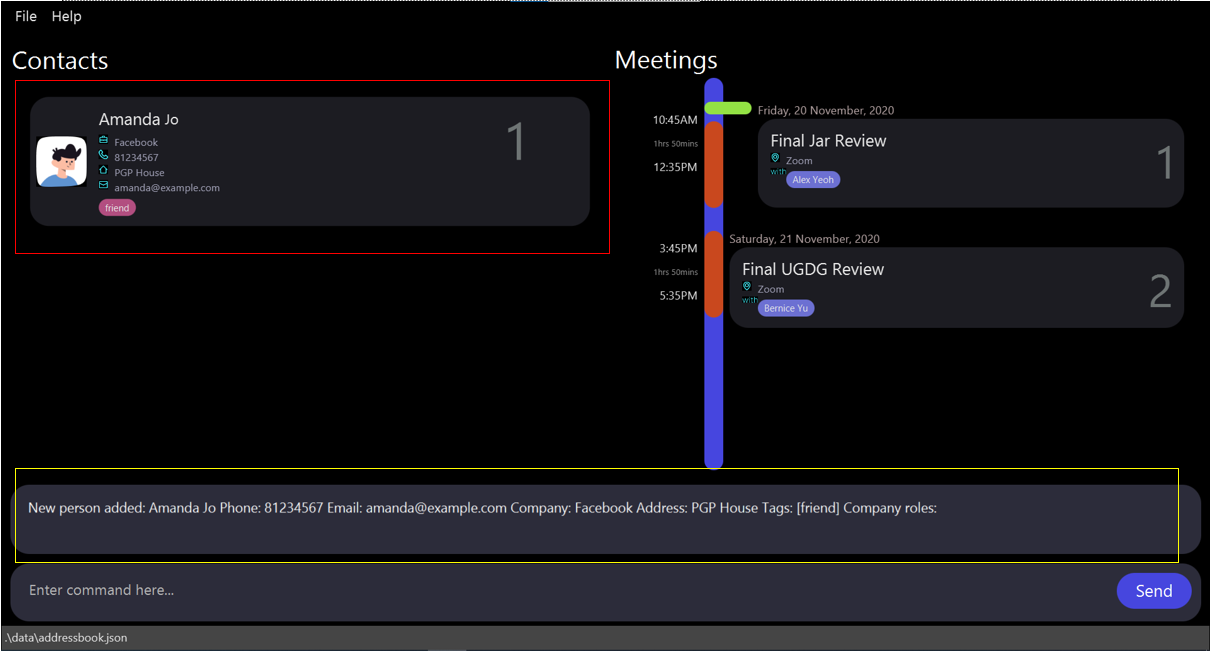
addcontact n/Amanda Jo p/81234567 e/amanda@example.com a/PGP House c/Facebook t/friend
Expected result:
New person added: Amanda Jo Phone: 81234567 Email: amanda@example.com Company: Facebook Address: PGP House Tags: [friend] Company roles:
will be shown as a feedback. The newly added contact being displayed on screen.
Example Usage Visual Walkthrough Guide:
State of the app BEFORE the command.
State of the app BEFORE the command.
4.1.2 Listing all persons: listcontact
done by: Koh Zhe Hao
One of the most basic commands that displays the list of all contacts in Recretary.
Format: listcontact
Example Usage
listcontact
Expected result:
Listed all persons
is shown as a feedback. All existing contacts will be displayed.
Note: Since this command’s behavior is very simple, the Visual Walkthrough Guide is omitted here.
listcontact keyword will be ignored by the application.
4.1.3 Editing a person: editcontact
done by: Zhao Huan
Ensure the validity of contacts’ data by updating personal information using the editcontact command. You can easily manage all data fields of your contacts in Recretary, no need to remove it and add again!
Format: editcontact INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [c/COMPANY] [t/TAG]… [r/COMPANY_ROLE]…
- This command edits the person at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the person list being displayed . The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - At least one of the optional fields should be provided. Recretary may be confused if a contact remains changed after edition.
- Existing values of a contact, if any, will be updated to the input values. And all meetings the contact is participating, if any, will be updated accordingly.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the person will be removed i.e adding of tags is not cumulative. - You can remove all the person’s tags by typing
t/ with no following tags.
Examples:
-
editcontact 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the 1st person to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively. -
editcontact 2 n/Betsy Crower t/Edits the name of the 2nd person to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags.
Example Usage
editcontact 1 n/Kelly Low e/kelly@example.com
Expected result:
Edited Person: Kelly Low Phone: 98764432 Email: kelly@example.com Company: ABC Holdings Pte. Ltd Address: John street, block 123, #01-01 Tags: Company roles:
Note: Since this command’s behavior is very similar to addcontact, the Visual Walkthrough Guide is omitted here.
4.1.4 Finding persons: findcontact
done by: Adithya Narayan Rangarajan Sreenivasan
Reduce distractions and other unnecessary contacts and information by filtering the contact list using the findcontact command. This command narrows down the list to only contacts whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: findcontact KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
hanswill matchHans - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans - Only the name is searched.
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
Hanwill not matchHans - Persons matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang
Examples:
-
findcontact Johnreturnsjohn chanandJohn Doe -
findcontact bernice davidreturnsBernice YuandDavid Li
Example Usage
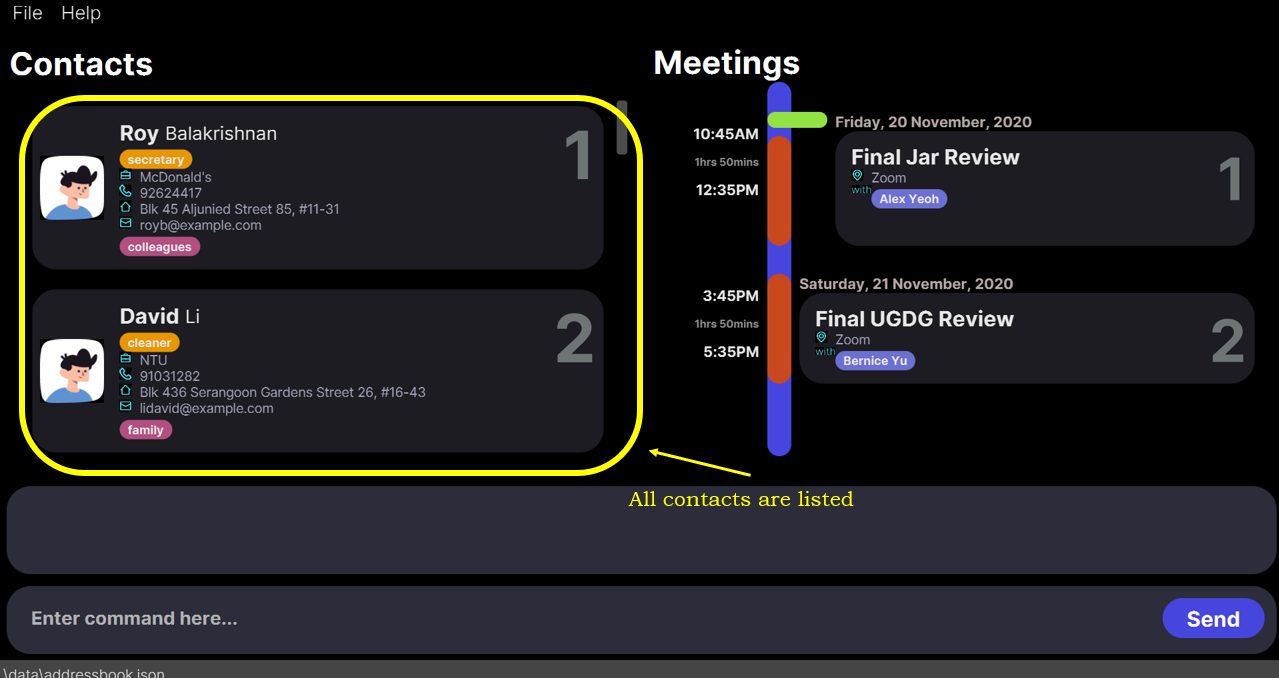
findcontact abc
Expected result
1 persons listed!
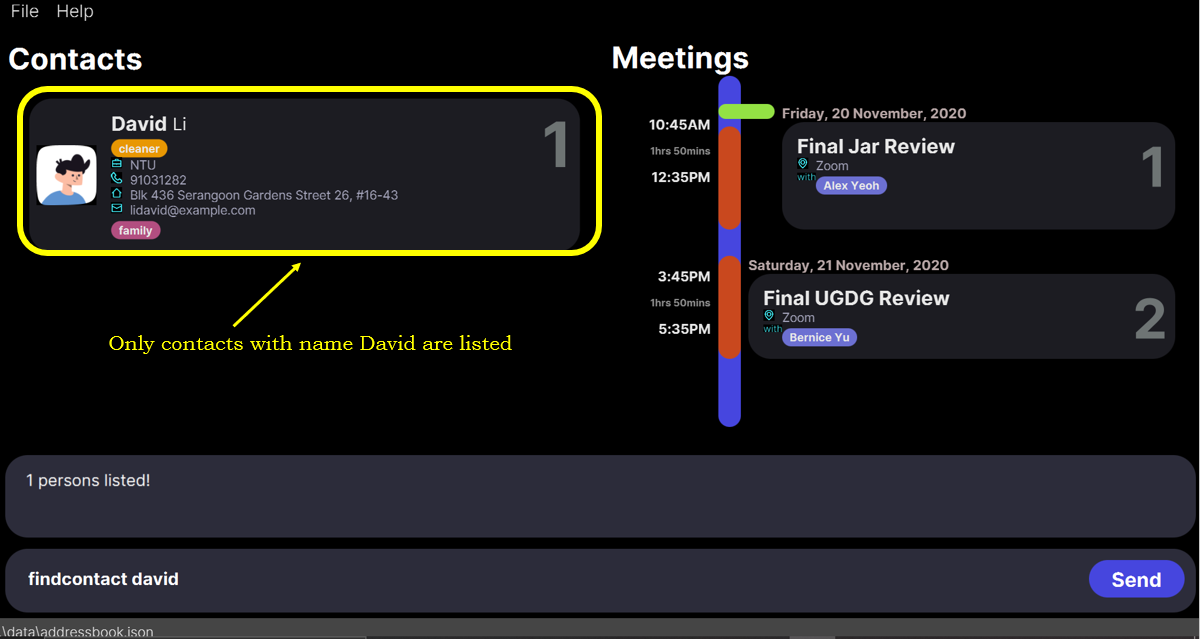
findcontact david command.
State of the app AFTER the
findcontact david command.
4.1.5 Deleting a person: deletecontact
done by: Zhao Huan
Reduce distractions and tidy up the application by removing contacts that are no longer needed using the deletecontact command. This command deletes the specified contact from the address book.
Format: deletecontact INDEX
- Deletes the person at the specified
INDEX. The INDEX has a similar behavior as the one in editcontact, i.e. an positive index of a contact from the list being displayed.
Examples:
-
deletecontact 2deletes the 2nd contact in the address book. -
findcontact Betsyfollowed bydeletecontact 1deletes the 1st contact in the resulting displayed list of thefindcontactcommand.
Example Usage
deletecontact 1
Expected result
Deleted Person: Kelly Low Phone: 98765432 Email: kelly@example.com Company: ABC Holdings Pte. Ltd Address: John street, block 123, #01-01 Tags: Company roles:
4.1.6 Clearing all contacts: clearcontact
done by: Liu Chuyue
Clears all contacts from the address book. If you enter anything following the clearcontact keyword, e.g. clearcontact 2, the extra input will be ignored by the application.
Format: clearcontact
Example Usage
clear contact
Expected result:
Contacts have been cleared!
Remove all existing contacts from Recretary. You can now see an empty contact list.
undo function!
4.2 Meeting Management
Meeting entries in Recretary have multiple attributes: date time, duration, title and location. You can declare the recurrence of a meeting to avoid repetitive input, and you can also add contacts as participants of a meeting. All meeting information will be displayed on the right-hand-side of the window, ordered by their starting time, with a green bar indicating the next upcoming meeting. When the next upcoming meeting starts, the green bar will move to the next meeting automatically, if any.
4.2.1 Adding a meeting: addmeeting
done by: Tan Xuan Zhi
Adds a meeting into the meeting schedule.
Format: addmeeting title/TITLE d/DATETIME dur/DURATION l/LOCATION [rec/RECURRENCE]
-
The format for
DATETIMEisd/M/yy HHmm.
e.g.d/1/11/20 1430e.g.d/1/1/20 1430e.g.d/12/11/20 1430 -
DATETIMEcannot overlap with any of the existing meetings. -
The format for
DURATIONisH mm, whereHandmmmust be non-negative numbers and cannot both be zero.
e.g.dur/1 30. -
The number of minutes in
DURATIONcannot exceed59. -
The field
RECURRENCEconsists of two parts separated by/. The first part can be one ofdaily,weeklyormonthlyindicating the frequency of recurrences, and the second part is a positive integer no more than 20 to indicate the number of recurrences.
e.g.daily/1, e.g.weekly/20, e.g.monthly/5
Example:
addmeeting title/roundtable discussion d/31/12/20 1200 dur/00 30 l/NUS SoCaddmeeting title/abc company meeting d/31/12/20 1400 dur/00 50 l/John street, block 123, #01-01 rec/weekly/5
Example usage:
addmeeting title/v1.5 discussion d/12/12/20 1200 dur/02 00 l/Home
Expected result:

New meeting added: v1.5 discussion Date and Time: 12 Dec 2020 12.00pm Duration: 2hrs Location: Home Recurrence: Participants: none
Add participants with the addpart command now!
Adds a new meeting on the meeting panel on the right. The existing list of meetings is automatically sorted after the addition according to date and time.
4.2.2 Adding a participant into a meeting: addpart
done by: Tan Xuan Zhi
Adds a participant into a meeting.
Format: addpart ci/CONTACT_INDEX mi/MEETING_INDEX
- Add the participant at the specified
CONTACT_INDEXto a meeting at the specifiedMEETING_INDEX. TheCONTACT_INDEXandMEETING_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the currently displayed contact list and meeting list respectively.
Examples:
-
addpart ci/1 mi/3adds the first contact in the whole list to the 3rd meeting. -
findcontact alicefollowed byaddpart ci/1 mi/2adds the first contact of thefindcontactcommand’s result into the 2nd meeting.
Example Usage:
addpart ci/1 mi/1
Expected result:
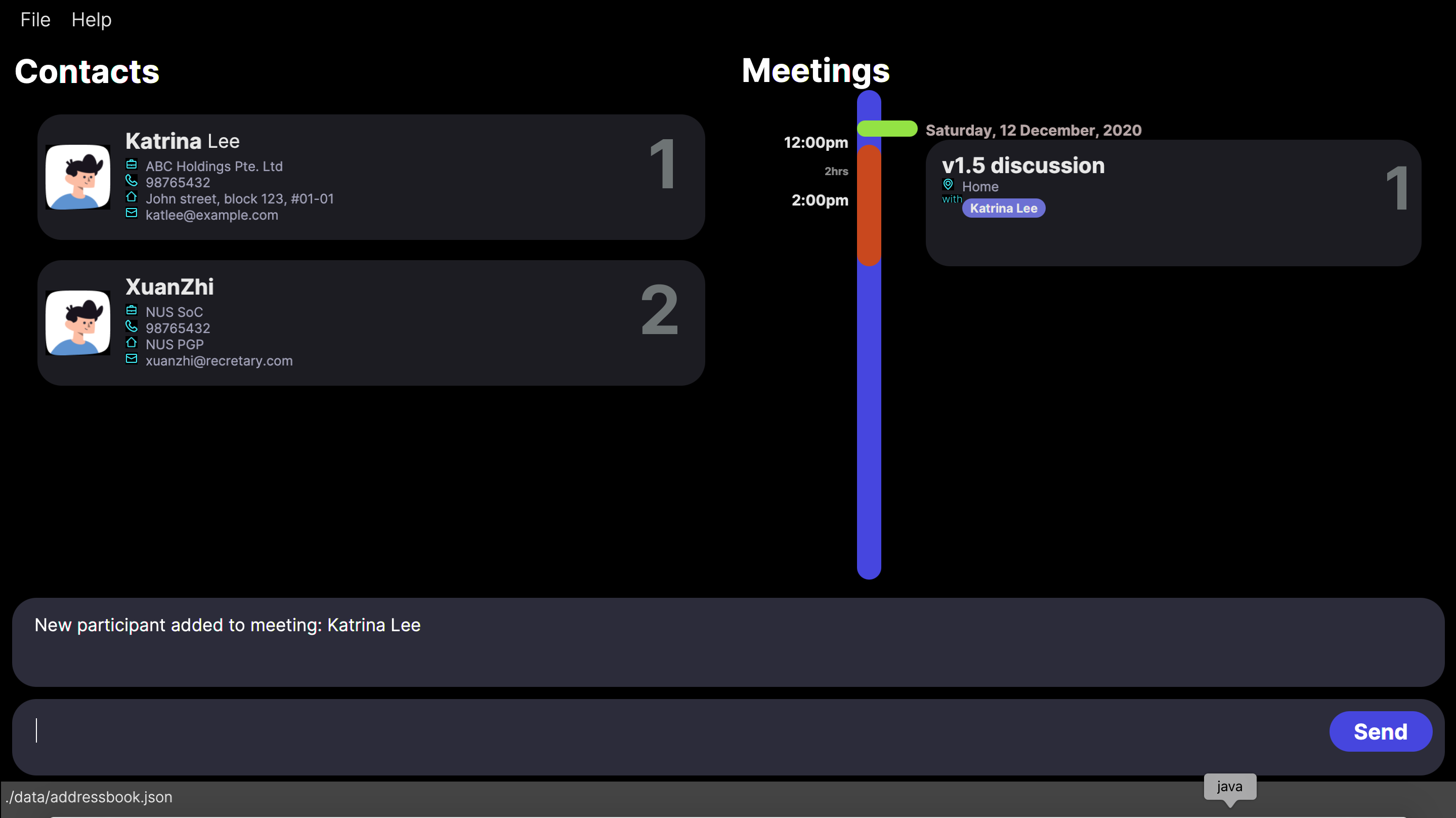
New participant added to meeting: NAME_OF_PARTICIPANT_ADDED
findcontact command before running an addpart to narrow the contact list so that you can easily add a contact instead of scrolling through the whole list!
Likewise, run a findmeeting command before running an addpart to narrow the meeting list so that you can easily add a meeting without scrolling through the whole list!
4.2.3 Delete a participant into a meeting: deletepart
done by: Tan Xuan Zhi
Deletes a participant from a meeting.
Format: deletepart ci/CONTACT_INDEX mi/MEETING_INDEX
- Delete the participant at the specified
CONTACT_INDEXfrom a meeting at the specifiedMEETING_INDEX. TheCONTACT_INDEXrefers to the index of the participant in the meeting andMEETING_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the currently displayed meeting list.
Examples:
-
deletepart ci/1 mi/3removes the first participant from the third meeting.
Example Usage:
deletepart ci/1 mi/1
Expected result:
Participant is removed from meeting: NAME_OF_PARTICIPANT_DELETED
4.2.4 Listing all meetings: listmeeting
Shows a list of all meetings in the address book.
Format: listmeeting
- Any trailing words following the command will be ignored.
Example Usage
listmeeting
Expected result:
Listed all meetings
All existing meetings are listed.
4.2.5 Editing a meeting: editmeeting
done by: Tan Xuan Zhi
Edits an existing meeting in the meeting schedule.
Format: editmeeting INDEX [d/DATETIME] [title/TITLE] [l/LOCATION] ...
- Edits the meeting at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed meeting list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - The
RECURRENCEfield of a meeting is not modifiable - If a recurring meeting is edited, only the meeting at the specific
INDEXwill be modified. - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- For the optional fields that have been omitted, the values will be unchanged.
Examples:
-
editmeeting 1 d/10/11/20 1400 l/clementiEdits the datetime and location of the 1st meeting to be10/11/2020 1400andclementirespectively.
Example Usage:
editmeeting 2 title/DEF company meeting dur/00 30
Expected Outcome:
Edited Meeting: DEF company meeting Date and Time: 12 Dec 2020 12.00pm Duration: 30mins Location: Home Recurrence: Participants: none
Change the title and duration of the second meeting in the currently displayed meeting list to DEF company meeting
and 30mins respectively. Other attributes of the meeting remain unchanged.
4.2.6 Finding meetings: findmeeting
done by: Adithya Narayan Rangarajan Sreenivasan
Reduce distractions and other unnecessary contacts and information by filtering the contact list using the findcontact command. This command narrows down the list to only meetings whose data (matches title, date in all natural formats, location) contain any of the given keywords.
Format: findmeeting KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
discusswill matchDiscuss - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Shareholder Meetingwill matchMeeting Shareholder - Most fields (title, date, time and location) are searched.
- Meetings matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Shareholder Meetingwill returnShareholder Chat,Team Meeting - Date is matched using natural formatting. e.g.
Nov,Novemberand11will match meetings that take place in november. - Participants are not considered while matching.
Examples:
-
findmeeting abc defreturnsabc meeting,def meeting
Example Usage
findmeeting abc
Expected result
1 meeting listed!
findmeeting command.
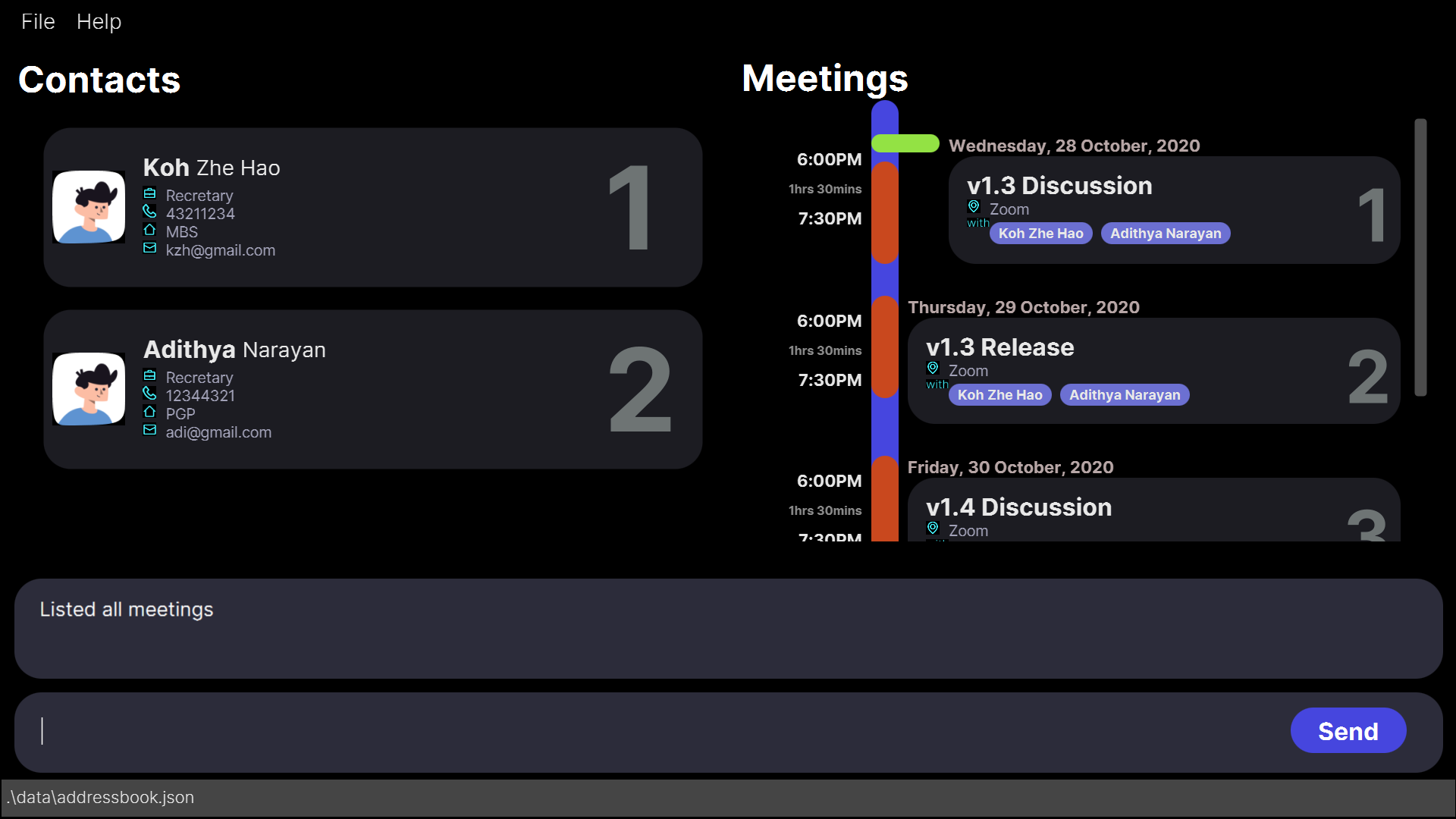
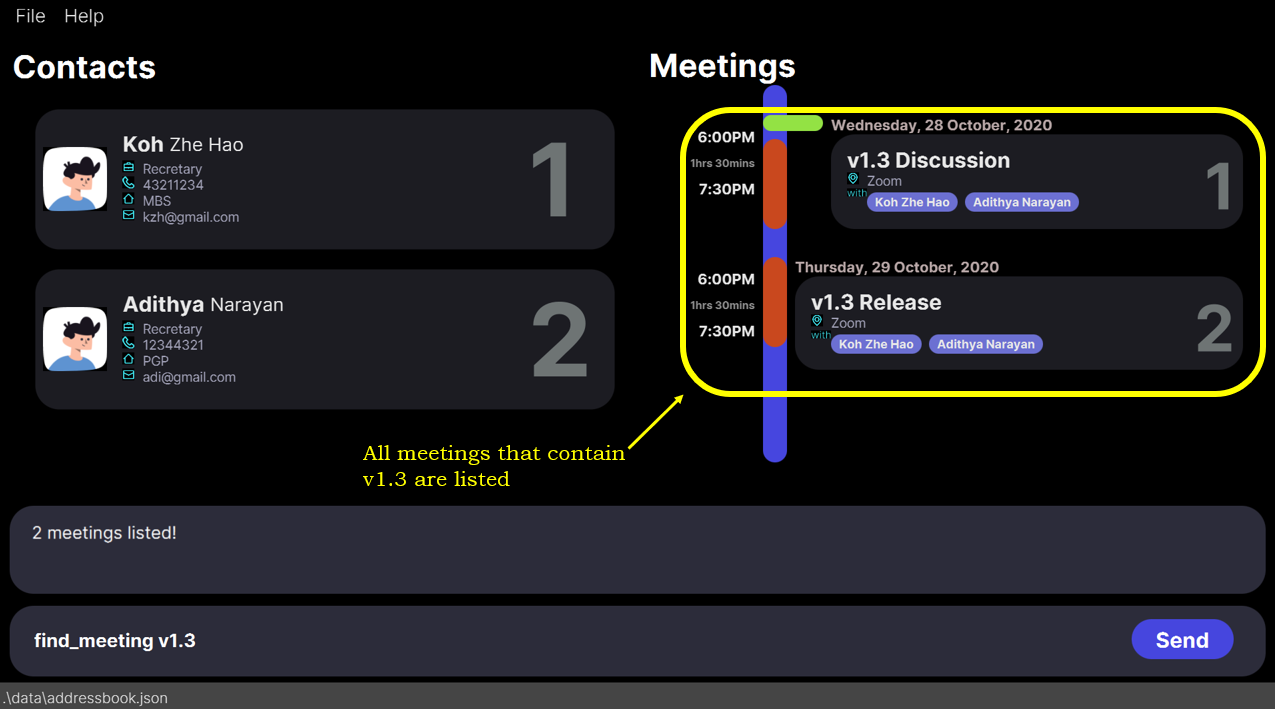
State of the app AFTER the
findmeeting v1.3 command.
4.2.7 Deleting a meeting: deletemeeting
done by: Zhao Huan
Reduce overhead by removing outdated or cancelled meetings to get better organized using the deletemeeting command! This command deletes the specified item (and its recurrences) from the address book.
Format: deletemeeting INDEX [rec/RECURRING]
- Deletes the meeting at the specified
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
- The recurring must be either
trueorfalse. If it’strue, the meeting specified and all its recurrences will be removed.
Examples:
-
deletemeeting 2deletes the 2nd meeting in the meeting schedule. -
deletemeeting 2 rec/truedeletes the 2nd meeting and all its recurrences in the address book. -
findmeeting Shareholderfollowed bydeletemeeting 1deletes the 1st meeting in the results of thefindmeetingcommand.
Example Usage
deletemeeting 3
Expected result:
Deleted Meeting: Annual meeting Date and Time: 31 Dec 2020 2.00pm Duration: 50mins Location: John street, block 123, #01-01 Recurrence: Participants: none
![]() Summary about recurring meetings:
Summary about recurring meetings:
- In
deletemeetingthere is an optional fieldrec/RECURRINGwhich may betrueorfalse.
e.g.rec/truemeans to delete all recurrences of the specified meeting. - In
addmeetingthere is an optional fieldrec/RECURRENCEwhich consists of two parts separated by/as mentioned above.
e.g.rec/weekly/5means the meeting added has recurs weekly for 5 times. - In
editmeeting, the recurrence field is not editable. Edition will only affect a specific instance.
4.2.8 Clearing all meetings : clearmeeting
Clears all meetings from the meeting schedule. Clears all contacts from the address book. If you enter anything following the clearmeeting keyword, e.g. clearmeeting 2, the extra input will be ignored by the application.
Format: clearmeeting
Example Usage
clearmeeting
Expected result:
Meetings has been cleared!
Remove all existing meeting from Recretary. You will now see an empty meeting list.
undo function!
4.2.9 Remind meetings: remindmeeting
done by: Koh Zhe Hao
One of the advanced commands in Recretary. It searches and displays all meetings that will occur within the hours specify by the user.
Format: remindmeeting HOUR
- HOUR must be a positive integer, the range of this value is from 1 - 2147483647 (user most likely won’t have so many data to keep track of in a practical usage).
Examples:
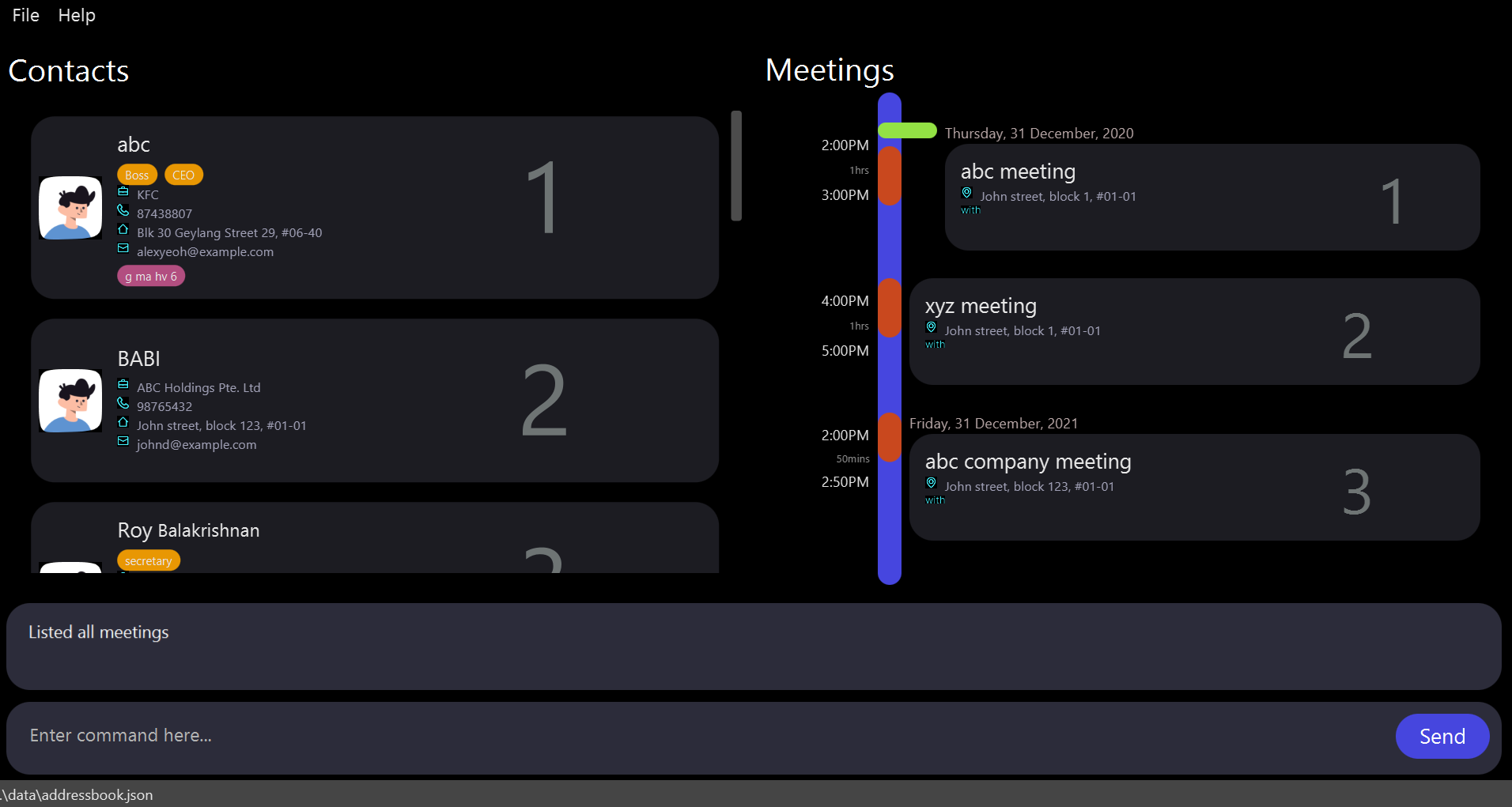
-
remindmeeting 1440returnsabc meeting,xyz meeting
Remark: 1440 = 2(months) * 30(days) * 24(hours) which is the total hours for two months; user can use this strategy to standardize the unit of time(hours) beforehand. The example describes the situation where user wants to find all meetings that will occur within two months.
remindmeeting command.
 State of the app AFTER the
State of the app AFTER the remindmeeting 1440 command.
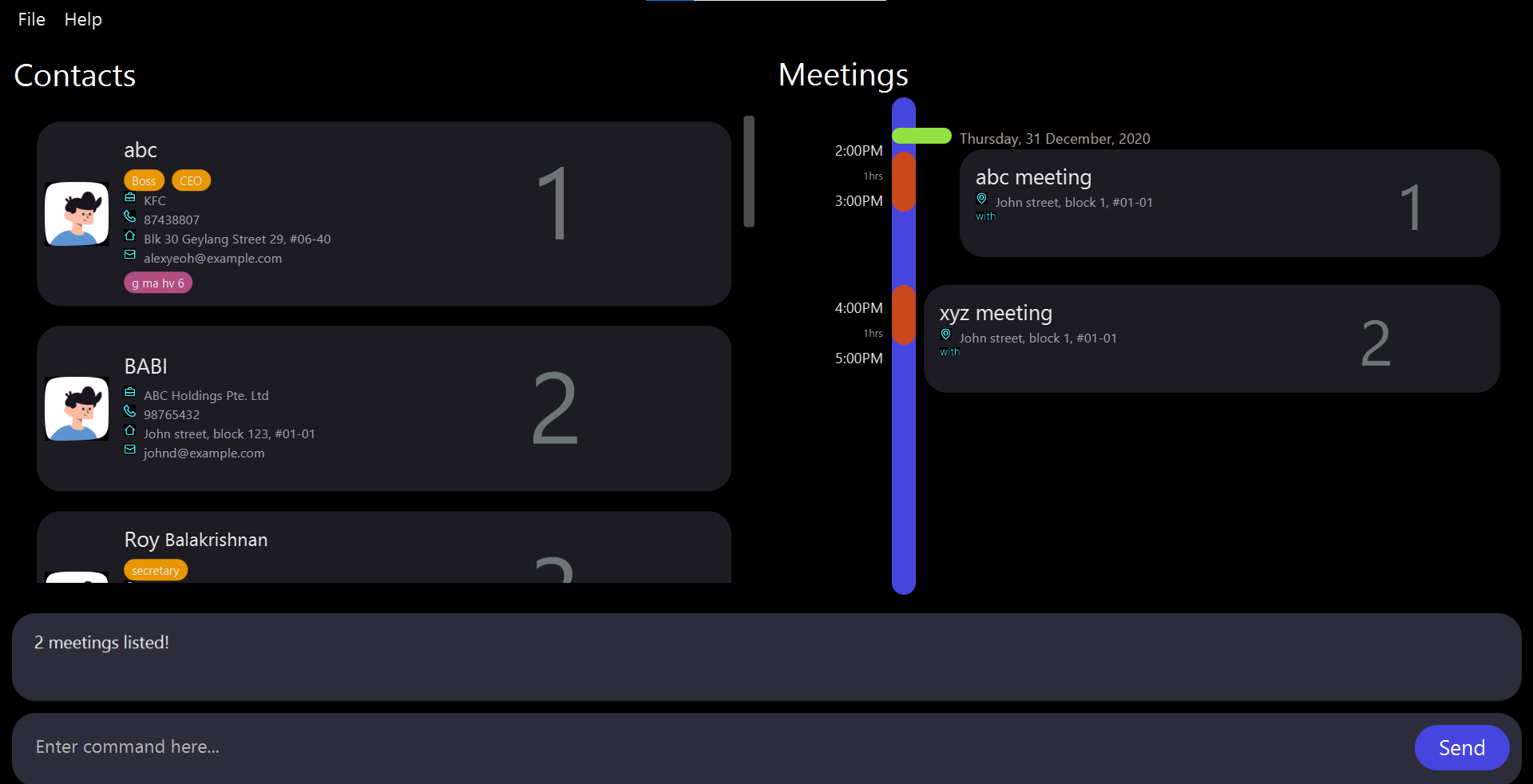
Note: The abc company meeting get filtered out(not displayed) because it will occur in 2021 which is way more than two months.
4.2.10 Exporting meetings in .ics format : exportmeeting
done by: Liu Chuyue
Exports all meetings as an iCalendar file that can be imported into other calendar apps such as Google Calendar.
Format: exportmeeting
- If you enter anything after the command, such as
exportmeeting 2, the extra input will be ignored. By default, the resulting file can be found in thedatafolder. Check the FAQ section to see how to change the save location. - You can simply click to open the file to import your meeting schedule into the calendar app on your computer, or upload it on any online calendar site.
Example Usage
exportmeeting
Expected result:
Meetings have been exported as .ics!
Export all existing meetings into a .ics file that can be find in the same folder of Recretary.
4.2.11 Automatic meeting reminder
done by: Zhao Huan
Pop up a meeting reminder if the earliest meeting is about to happen so that you can avoid forgetfulness! This is an automatic task and no command is needed to activate the reminder. However, in case you are not sure about future meetings, you can always use the remindmeeting command in 4.2.9 to view upcoming meetings.
Below is an illustration of the pop-up reminder:

![]() About pop-up time:
About pop-up time:
- The reminder will pop up 30 minutes in advance for the start time of the ealiest upcoming meeting.
- If the start time of the earliest future meeting is already within 30 minutes when the app starts, a reminder will popup one minute later.
5 General
5.1 Viewing help : help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page. Anything following the help keyword will be ignored by the application.
5.2 Undo : undo
done by: Adithya Narayan Rangarajan Sreenivasan
Undoes the previous command or previous n commands based on the given index.
Format: undo [INDEX]
![]() Notes about the undo command:
Notes about the undo command:
-
undocommand is purposefully left out of the history and is hence not undoable. This is because you can undo previous commands before the undo to prevent being stuck in an undo loop. -
exportmeetingcommand cannot be undone as it exports outside the app scope.
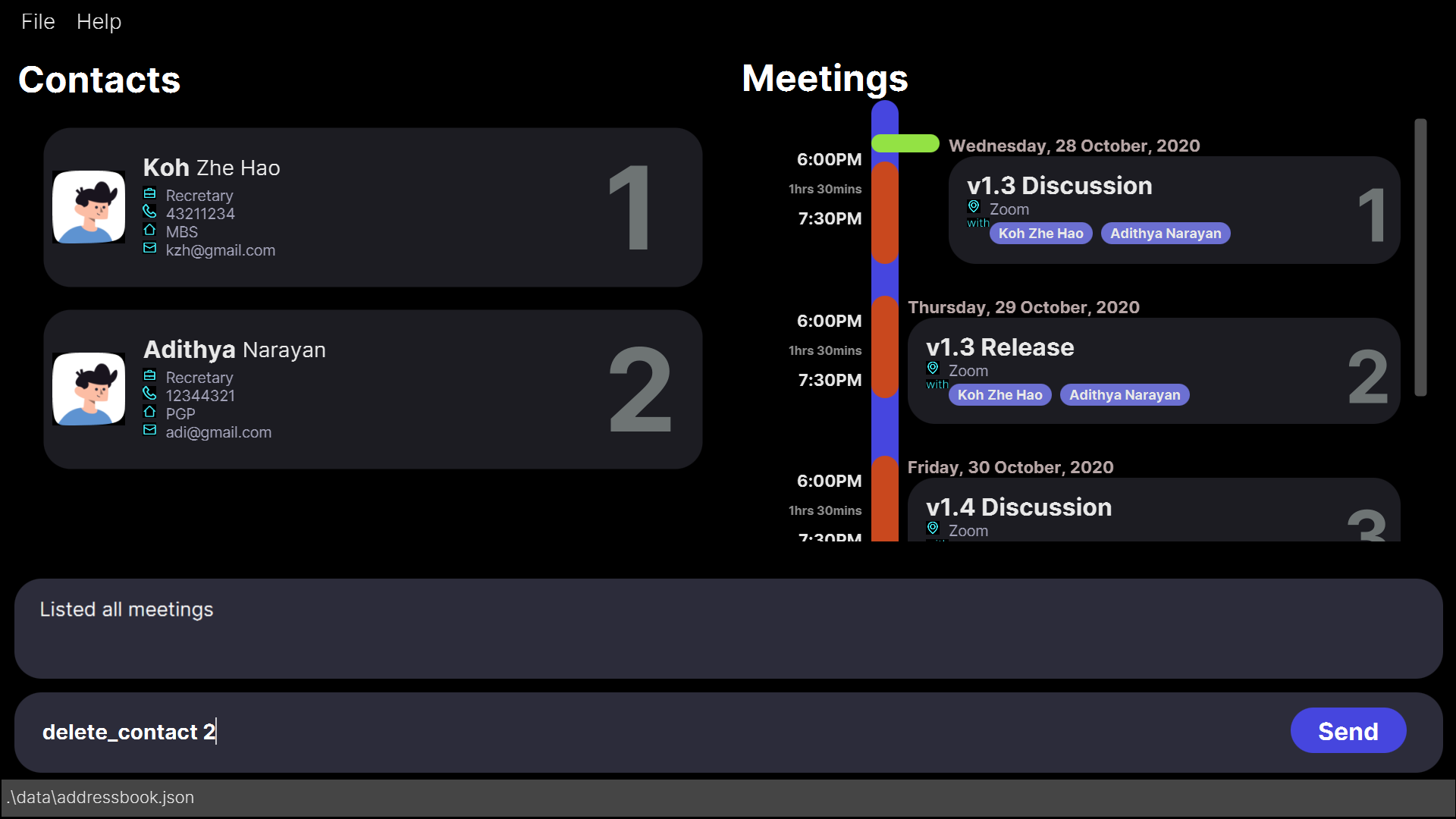
1. State of the app BEFORE the
deletecontact command that you entered by mistake and wish to undo.
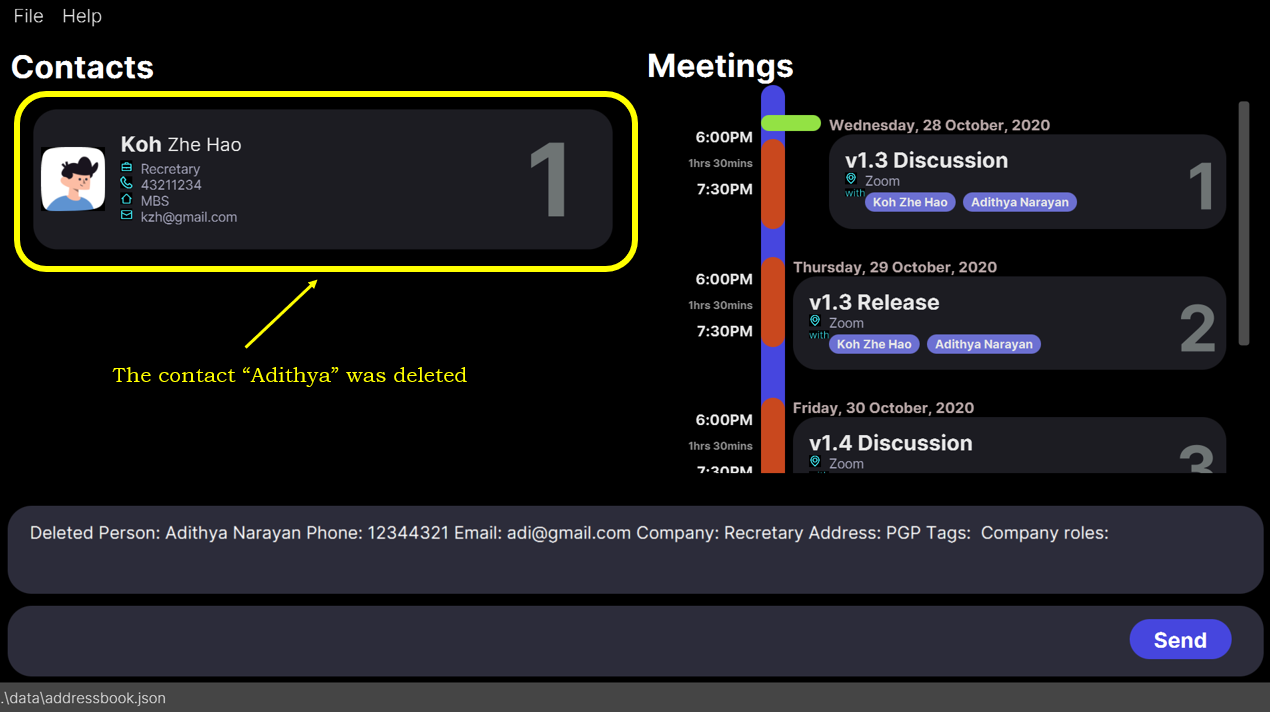
2. State of the app AFTER the
deletecontact command that you entered by mistake and wish to undo.
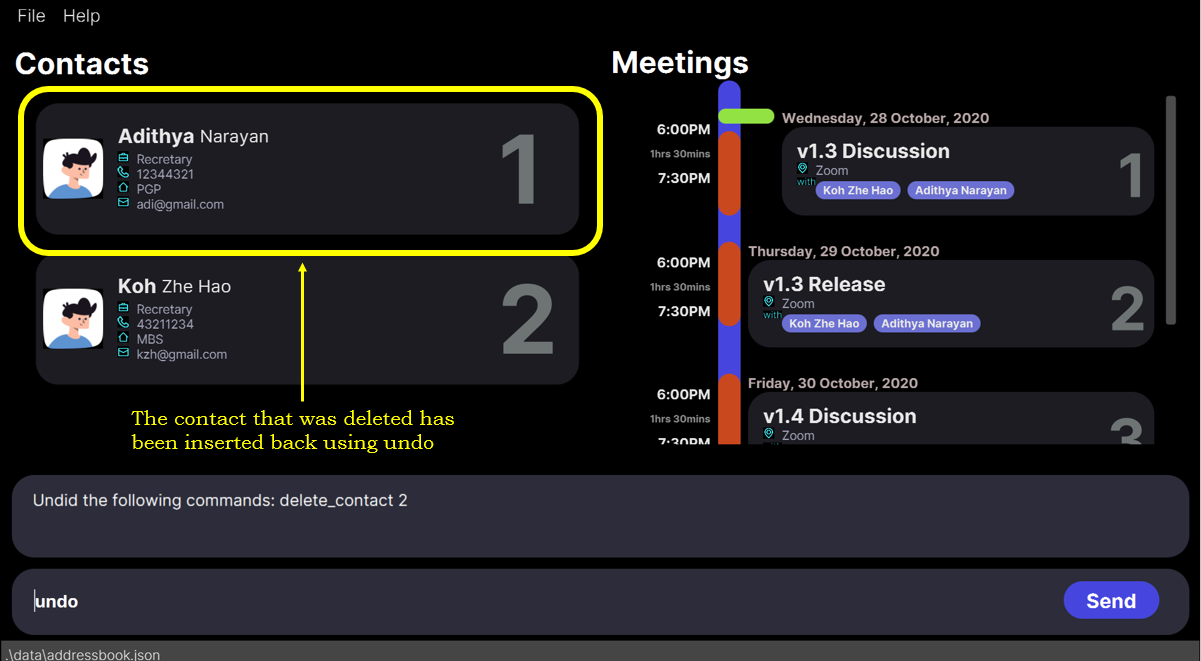
3. State of the app AFTER the
undo command.
5.3 Command Session History
done by: Adithya Narayan Rangarajan Sreenivasan
You can easily scroll up and down through the list of previous successful commands using the UP and DOWN key on your keyboard while in the command box.
![]() Notes about the command session history:
Notes about the command session history:
- Only successful previous commands (commands that did not give an error), are stored in the command history. This decision was taken deliberately because of the fact that if there is an error in the command, the command doesn’t disappear but it stays in the command box highlighted in red.
- Be cautious as your current command is wiped out when you move up or down (similar to the windows command prompt).
5.4 Update user preference : edituserpref
done by: Koh Zhe Hao
- Edit the value of interval(check out glossary for more information) between meetings. The interval value is stored and remain valid when user open the app next time.
- The dafault value(if user dont specify its value via this command) is 0 which means that interval is not considered.
-
i/INTERVALindicates the interval between meetings. Note that there is a range restriction similar to theremindmeetingcommand. - Take note of the user feedback in the box AFTER the
edituserpref i/10command.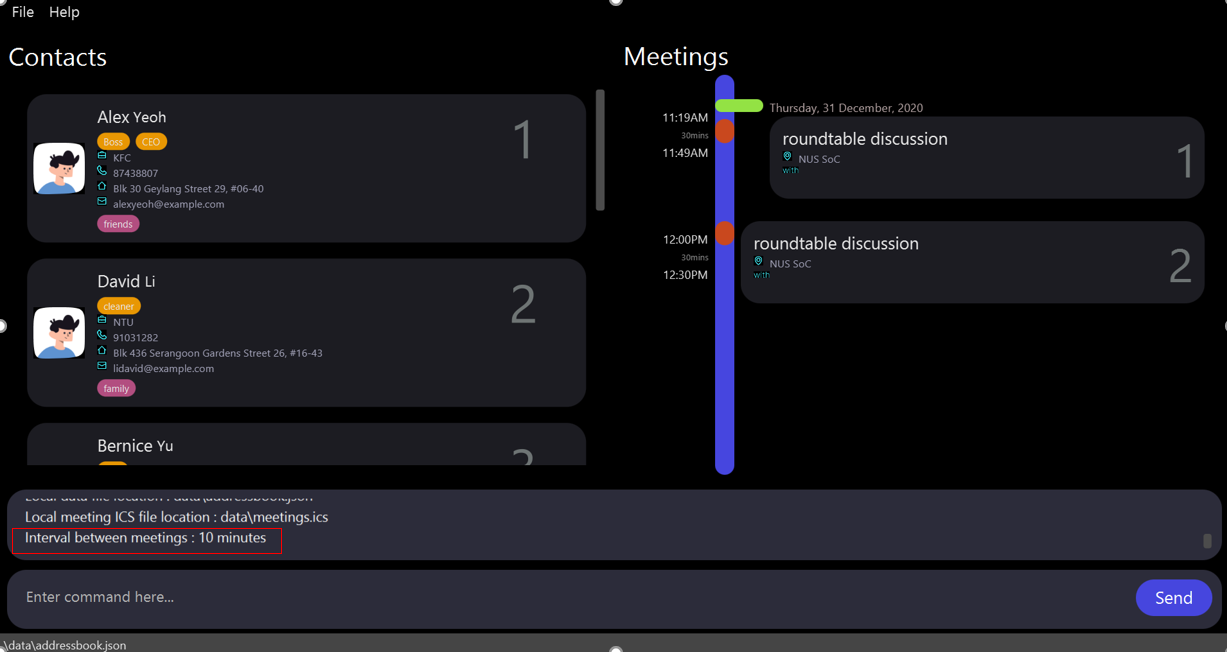
5.5 Viewing previous commands
Pressing the up arrow key will change the content of the input box to the previous command that was executed (if one exists). Similarly, pressing the down arrow will display the command that was executed after the current one. Press an arrow key multiple times to navigate through multiple commands.
![]() Notes about viewing previous/later commands:
Notes about viewing previous/later commands:
- Only commands that were successfully executed can be viewed.
- If there is any text in the input box when an arrow key is pressed, it will be cleared and cannot be navigated back to.
5.6 Saving the data
Recretary data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
5.7 Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program. Anything following the exit keyword will be ignored by the application.
Format: exit
6 FAQ
done by: Liu Chuyue
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: To transfer your data to another Computer:
- Install the app in the other computer.
- Transfer the following files to the other computer:
- The
datafolder in the same folder as the JAR file - The file named
config.json - The file named
preferences.json
- The
- Place these files in the same folder as the Recretary.jar file in the new computer.
- Run Recretary as normal.
- Your data should be successfully transferred over.
Q: Where is my Recretary data stored?
A: By default, a data folder will be created in the same folder as the Recretary.jar file. After running the app for the first time, you can change the file path by directly editing preferences.json, which will also be created in the same folder.
7 Command summary
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| General Commands | |
| Help | help |
| Exit | exit |
| Undo |
undo [INDEX] e.g., undo 3 or undo
|
| Edit user preference |
edituserpref i/INTERVAL e.g., edituserpref i/10
|
| Contacts | |
| Add |
addcontact n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS c/COMPANY [r/COMPANY_ROLE] [t/TAG]… e.g., addcontact n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd a/XYZ Company r/manager t/friend
|
| Delete |
deletecontact INDEX e.g., deletecontact 3
|
| Edit |
editcontact INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [c/COMPANY] [r/COMPANY_ROLE] [t/TAG]…e.g., editcontact 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com
|
| Find |
findcontact KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., findcontact James Jake
|
| List | listcontact |
| Clear | clearcontact |
| Meetings | |
| Add |
addmeeting d/DATETIME dur/DURATION title/TITLE l/LOCATION [rec/RECURRENCE] e.g., addmeeting d/31/12/20 1400 dur/01 00 title/xyz meeting l/John street, block 1, #01-01 rec/weekly/5
|
| Add Participant |
addpart ci/INDEX mi/INDEXe.g., addpart ci/1 mi/3
|
| Delete Participant |
deletepart ci/CONTACT_INDEX mi/MEETING_INDEX e.g., deletepart ci/1 mi/3
|
| Delete |
deletemeeting INDEX [rec/RECURRING]e.g., deletemeeting 5 rec/true
|
| Edit |
editmeeting INDEX [d/DATETIME] [dur/DURATION] [t/TITLE] [l/LOCATION]e.g., editmeeting 1 dur/01 30 l/COM2 LT17
|
| Find |
findmeeting KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., findmeeting recretary stakeholders
|
| List | listmeeting |
| Clear | clearmeeting |
| Remind |
remindmeeting HOUR e.g., remindmeeting 24
|
| Export | exportmeeting |
8 Prefix summary
| Prefix | Commands | Description |
|---|---|---|
| i/ | edituserpref |
interval between meetings |
| n/ |
addcontact, editcontact
|
name of a contact |
| p/ |
addcontact, editcontact
|
phone number of a contact |
| e/ |
addcontact, editcontact
|
email of a contact |
| a/ |
addcontact, editcontact
|
address of a contact |
| c/ |
addcontact, editcontact
|
company of a contact |
| r/ |
addcontact, editcontact
|
company role of a contact |
| t/ |
addcontact, editcontact
|
tag of a contact |
| d/ |
addmeeting, editmeeting
|
date and time of a meeting |
| l/ |
addmeeting, editmeeting
|
location of a meeting |
| ci/ |
addpart, deletepart
|
index of contact |
| mi/ |
addpart, deletepart
|
index of meeting |
| dur/ |
addmeeting, editmeeting
|
duration of a meeting |
| rec/ |
addmeeting, deletemeeting
|
recurrence of a meeting |
| title/ |
addmeeting, editmeeting
|
title of a meeting |
9 Glossary
done by: Liu Chuyue
- CLI: Command Line Interface. A program that accepts text input to execute system functions.
- Company Role: The position of a contact plays in their company.
- GUI: Graphic User Interface. A system of interactive visual components for computer software.
-
iCalendar: A file type that allows storing and accessing calendar and sheduling information. It usually has the file extension of
.ics. - Interval: This represents the minimum time gap between meetings. It is meant to represent travelling time or resting time in between meetings.